Weaver Lab - Homepage

Center for Bioengineering & Tissue Regeneration
Valerie M. Weaver Lab

Center for Bioengineering & Tissue Regeneration
Valerie M. Weaver Lab
Center for Bioengineering & Tissue Regeneration
Valerie M. Weaver Lab

Center for Bioengineering & Tissue Regeneration
Valerie M. Weaver Lab

Center for Bioengineering & Tissue Regeneration
Valerie M. Weaver Lab

Center for Bioengineering & Tissue Regeneration
Valerie M. Weaver Lab
Publications
Our Research
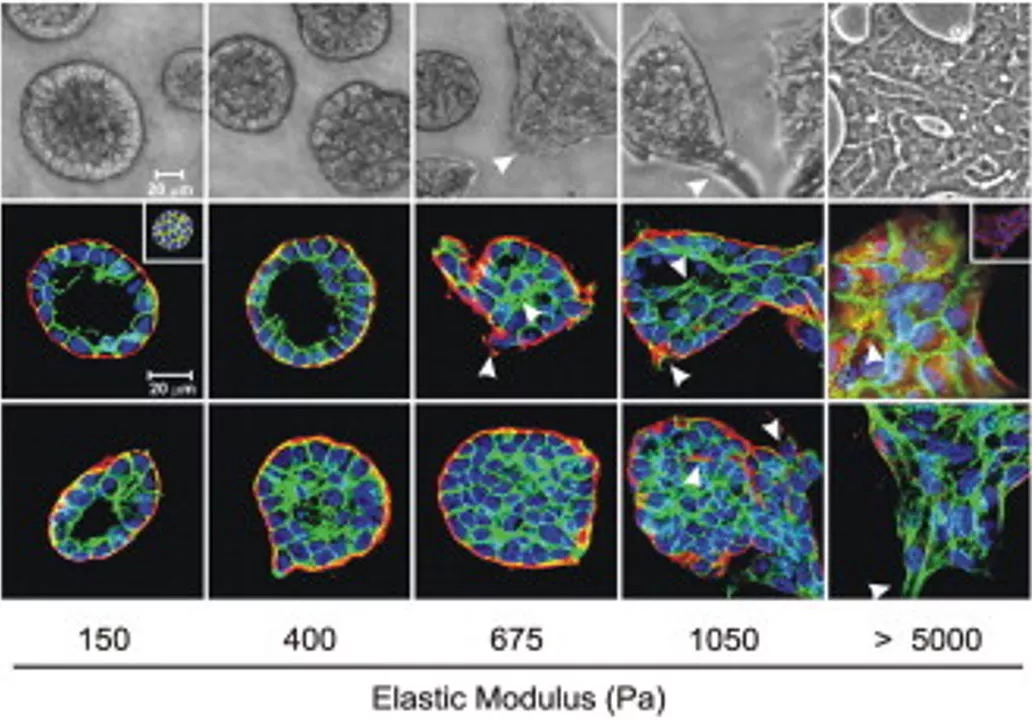
Epithelial tissue morphogenesis proceeds within the context of a three dimensional (3D) extracellular matrix (ECM). Accordingly, to clarify
...
The transition of the mammary epithelium to a metastatic state is an important event that drastically increases mortality
...
Stromal-epithelial interactions drive development and maintain tissue homeostasis through a network of soluble and insoluble factors that operate
...
Human embryonic stem cell (hESc) lines are likely the in vitro equivalent of the pluripotent epiblast. hESc express
...
Featured News

Dr. Valerie Weaver Receives NCI Outstanding Investigator Award (OIA) and $6.7M R35 Grant
Read full story
Please follow the link to Twitter to view the @UCSFSurgery Twitter site.


 PubMed
PubMed